To better understand the disruption caused by the
actions of psychoactive drugs, a general knowledge of the normal functioning of
the nervous system’s basis unit, the neuron, is required.
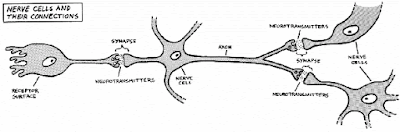
First, stimuli from the internal or external
environment are received by the appropriate sensory receptor, perhaps an organ
such as an eye or an ear. Once sensed,
these stimuli are converted into electrical impulses. The impulses are then directed along the axon
toward the synaptic junction near an adjacent neuron.
On arrival at the synapse, the electrical impulses
stimulate the production and release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters
transmit the electrical impulses from one neuron to the dendrites of adjoining
neurons. Thus neurons function in a
coordinated fashion to send information to the brain for interpretation and to
relay appropriate response commands outward to the tissues of the body.
The
role of neurotransmitters is critically important to the relay of information
within the system. A substance that has
the ability to alter some aspect of transmitter function has the potential to
seriously disrupt the otherwise normally functioning system. Psychoactive drugs are capable of exerting
these disruptive influences on the neurotransmitters work, often by blocking
the production of a neurotransmitter or forcing the continued release of a
neurotransmitter.













No comments:
Post a Comment