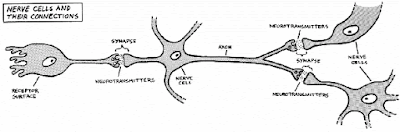
To better understand the disruption caused by the
actions of psychoactive drugs, a general knowledge of the normal functioning of
the nervous system’s basis unit, the neuron, is required.
First, stimuli from the internal or external
environment are received by the appropriate sensory receptor, perhaps an organ
such as an eye or an ear. Once sensed,
these stimuli are converted into electrical impulses. The impulses are then directed along the axon
toward the synaptic junction near an adjacent neuron.